MicroRNA research has revolutionized our understanding of gene regulation, particularly since the groundbreaking discoveries made by Nobel laureate Gary Ruvkun in 1992. His work with the C. elegans roundworm unveiled a new dimension of genetic control that is critical not only in basic biology but also in the development of microRNA therapies for diseases like cancer and heart disease. This fledgling field, initially met with skepticism, gained momentum thanks to significant federal funding research, allowing scientists to delve deeper into the role of these tiny RNA molecules. Today, as clinical trials for microRNA-based therapies unfold, the excitement surrounding their potential therapeutic applications has skyrocketed within the scientific community. The early contributions of Ruvkun and his collaborators have sparked a widespread interest, demonstrating how understanding microRNA can offer groundbreaking insights into human health and disease.
Exploring the intricacies of small non-coding RNAs, termed microRNAs, unveils a profound layer of gene modulation that has vast implications for various fields of medicine and biology. Pioneers like Gary Ruvkun have significantly advanced the body of knowledge regarding these genetic regulators, especially in model organisms such as C. elegans. Their research highlights the essential role of microRNAs in translating genetic information into functional proteins, opening doors for innovative therapies aimed at treating chronic diseases. With robust support from federal funding initiatives, this branch of science continues to thrive, paving the way for transformative microRNA-related advancements. As we delve into this captivating subject, it becomes clear that the intersection of RNA biology and therapeutic development holds tremendous promise for future healthcare breakthroughs.
The Groundbreaking Discovery of MicroRNA by Gary Ruvkun
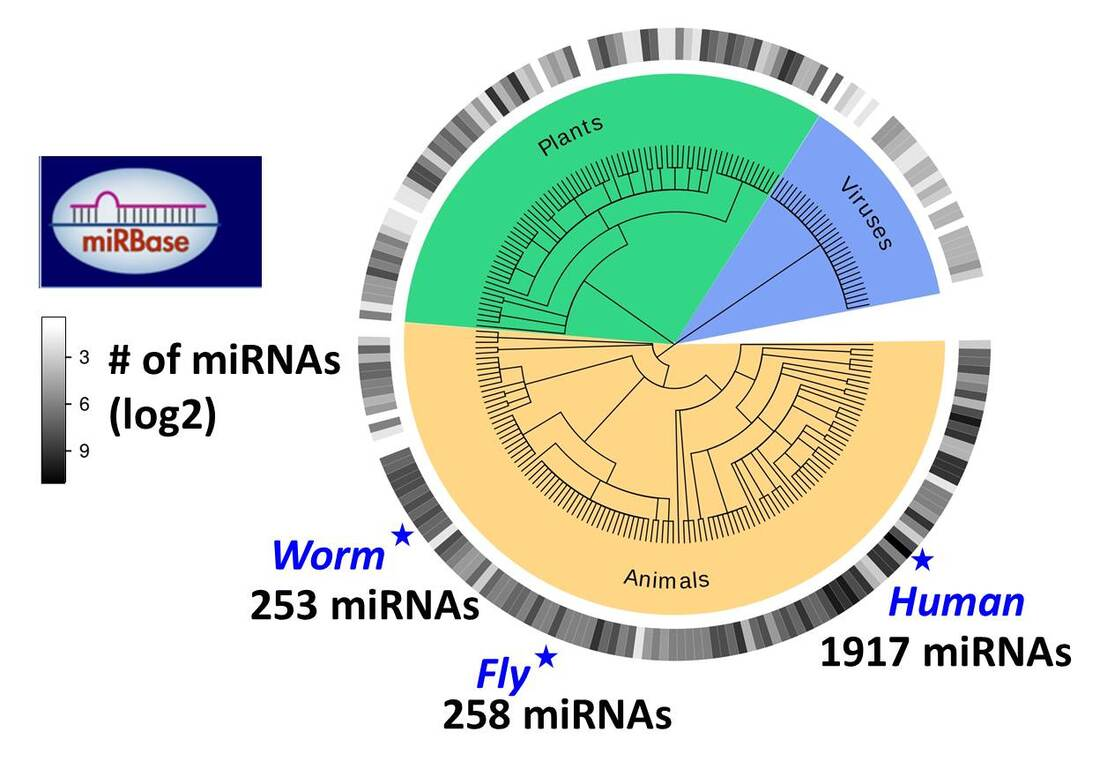
In 1992, Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros made a landmark discovery in the field of genetics with the identification of microRNA in the C. elegans roundworm. This groundbreaking work initially went unnoticed, as they were not widely recognized figures in the scientific community at that time. Their findings, published in the journal Cell a year later, introduced a new paradigm in gene regulation, emphasizing the role of these tiny RNA molecules in modulating gene expression. The impact of their work was primarily acknowledged within specific circles, mainly among RNA researchers and those fascinated by the biology of C. elegans, which serves as a key model organism in genetics.
Over the decades, Ruvkun’s revelation about microRNA regulation transitioned from a niche discovery to a cornerstone of molecular biology, influencing a myriad of research areas. This shift reflects the evolution of scientific understanding, with many researchers now recognizing the universal importance of microRNAs across various species, including humans. The increasing visibility of microRNA research has galvanized interest and funding, propelling it into the spotlight and solidifying its relevance for ongoing studies in gene regulation and therapeutic applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is microRNA research and why is it important?
MicroRNA research focuses on understanding the role of microRNAs, small non-coding RNA molecules, in gene regulation and development. It is crucial as microRNAs are involved in many biological processes and have implications for therapies in diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
How did Gary Ruvkun contribute to microRNA research?
Gary Ruvkun, along with Victor Ambros, discovered microRNAs in the early 1990s while studying C. elegans. Their groundbreaking research revealed a new level of gene regulation, laying the foundation for future studies and earning them the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024.
What are some current applications of microRNA therapies?
Current applications of microRNA therapies include treating various diseases such as heart disease, cancer, Crohn’s disease, and Alzheimer’s. These therapies are in clinical trials, showcasing the potential of microRNAs in modern medicine.
What is the link between federal funding research and microRNA studies?
Federal funding research has significantly supported microRNA studies, with many breakthroughs financed by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This funding has facilitated critical advances in understanding gene regulation through microRNAs.
How have microRNAs been shown to affect human health?
MicroRNAs have been shown to control the expression of about 1,000 genes in the human genome, influencing protein production and thus playing vital roles in cellular function and health. Their dysregulation is associated with various diseases, highlighting their importance in health research.
What role do microRNAs play in gene regulation?
MicroRNAs play a pivotal role in gene regulation by binding to messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and preventing protein production, thereby controlling the expression of genes. This process is fundamental to development, differentiation, and cellular responses.
Why was the initial response to the discovery of microRNAs muted?
Initially, the discovery of microRNAs by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros did not generate widespread excitement in the evolutionary biology community, as the significance of their findings for other species beyond C. elegans was not immediately clear.
How do microRNAs contribute to drug development?
MicroRNAs are instrumental in drug development as they help in identifying new therapeutic targets and understanding disease mechanisms. Companies focus on RNA interference therapeutics, a burgeoning field supported by foundational research in microRNA.
What is the impact of Gary Ruvkun’s research on today’s scientific landscape?
Gary Ruvkun’s research on microRNAs has profoundly impacted the scientific landscape, driving interest in RNA biology and leading to significant advancements in therapeutic strategies, illuminating the importance of federal funding in scientific innovation.
What challenges exist in the future of microRNA research?
Challenges in the future of microRNA research include securing sustained federal funding, as budget cuts could hinder essential studies and discourage young scientists from pursuing careers in this critical field of gene regulation.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Discovery of microRNA | In 1992, Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros discovered microRNA while studying C. elegans, which eventually led to the Nobel Prize in 2024. |
| Initial Reception | Their findings initially received lukewarm responses and were mainly recognized by a small community focused on RNA research. |
| Impact on Research and Medicine | MicroRNAs are now understood to be critical in gene regulation across species, with therapies in clinical trials for various diseases including cancer and Alzheimer’s. |
| Funding and Support | Ruvkun’s lab, primarily funded by the NIH, emphasizes the importance of government support for continuous scientific advancements. |
| Economic Contributions | Research has contributed to the growth of major pharmaceutical companies and highlights the role of federal funding in scientific and economic development. |
Summary
MicroRNA research has emerged as a pivotal field that enhances our understanding of gene regulation and its implications in medicine. The journey of microRNA, from its discovery by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in the early 1990s to receiving the Nobel Prize in 2024, underscores its importance in contemporary genetics. With ongoing clinical trials exploring microRNA-based therapies for diseases ranging from cancer to Alzheimer’s, the significance of this research continues to grow, revealing new frontiers in medical science. Support from federal funding has been critical in this journey, proving that investment in scientific research can yield substantial societal benefits.