The Franklin stove stands as a remarkable testament to the ingenuity of Benjamin Franklin, whose inventions have significantly shaped American history. This energy-efficient heating solution emerged during the harsh winter of 1740-1741, reflecting Franklin’s profound understanding of climate adaptation and environmental challenges. Historians like Joyce Chaplin have delved into this lesser-known invention, highlighting its role in reshaping how Americans approached indoor comfort and fire management. The Franklin stove not only revolutionized domestic heating but also contributed to the early discussions of environmental history and the science of meteorology. As we explore the legacy of Franklin’s scientific endeavors, we uncover the intricate connections between his innovations and the Enlightenment thinking that fueled a new era of discovery and progress.
Known for its role in improving home heating, the Franklin stove is a foundational innovation that embodies Franklin’s vision of scientific advancement. This heating device was conceived during a period marked by severe winters, illustrating early responses to environmental adversity. As Franklin’s inventions paved the way for enhanced living conditions, they underscored the relationship between technological progress and the evolving understanding of our climate. Moreover, through historical explorations, we see how this stove and other inventions categorized under Franklin’s prolific outputs offer critical insights into the history of science and climate resilience. Thus, the legacy of the Franklin stove extends beyond mere practicality, inviting us to comprehend its impact on American environmental history and society.
The Franklin Stove: A Revolutionary Invention
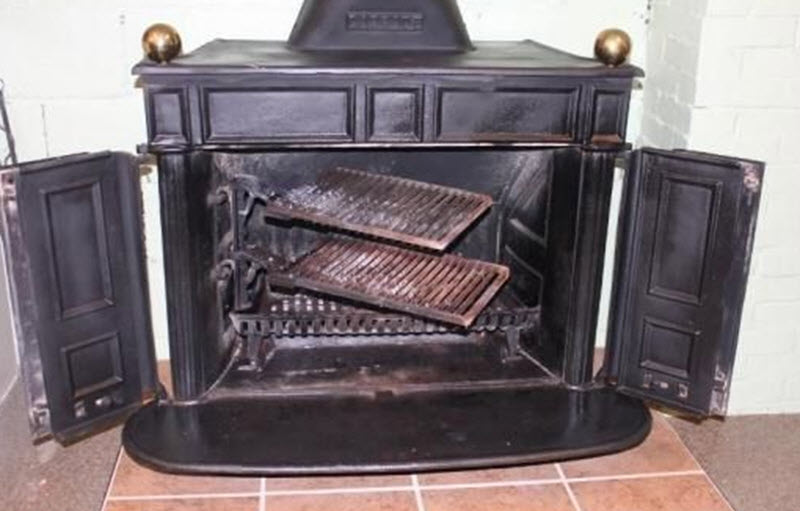
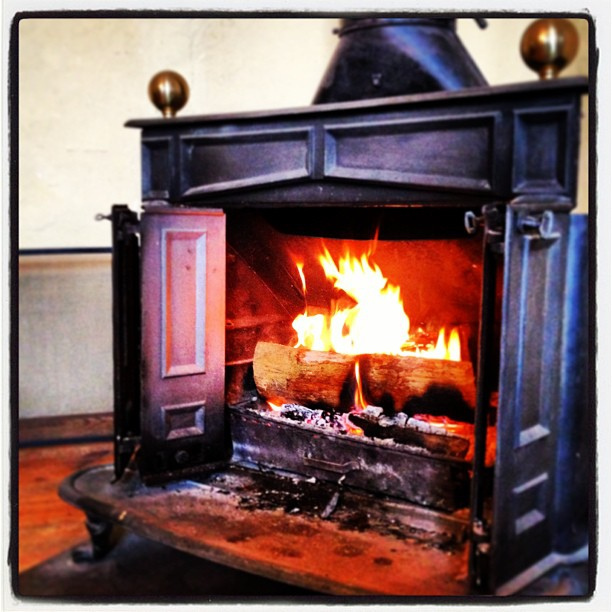
The Franklin stove, conceived by Benjamin Franklin in the early 18th century, represents a significant achievement in the realm of science and technology. Designed to improve indoor heating while reducing the amount of wood consumed, it symbolized Franklin’s innovative spirit. This invention not only enhanced comfort during the brutal winters of the Little Ice Age but also paved the way for future advancements in heating technology. Furthermore, it had a lasting impact on home design and energy consumption, highlighting the importance of efficiency in everyday life.
As Franklin meticulously crafted his stove, he drew connections between the experience of comfort indoors and the broader atmospheric conditions outside. His design principles incorporated a fundamental understanding of convection currents, which allowed warm air to circulate effectively within a room. This early exploration of how to manipulate air flow is indicative of the emerging field of environmental science, linking human comfort to atmospheric phenomena, an approach echoed in modern environmental history studies.
Joyce Chaplin’s Insights on Benjamin Franklin’s Innovations
In her compelling book, Joyce Chaplin uncovers the multifaceted nature of Benjamin Franklin’s genius. Unlike the popular image of Franklin as merely ‘Poor Richard,’ Chaplin paints a picture of a man deeply engaged with the scientific advancements of his time. She examines how Franklin’s inventions, including the stove, were not isolated but interconnected with societal needs and environmental challenges. Through her research, she illustrates the relevance of his work in today’s context, particularly in terms of climate adaptation and the innovative spirit that characterizes American history.
Chaplin’s narrative also highlights the lessons that can be drawn from Franklin’s life, particularly in relation to how science can address societal problems. Her exploration reveals that Franklin’s innovations were as much about improving individual comfort as they were about making a broader statement about human capability to harness technology for societal good. This message resonates strongly with contemporary issues as we navigate climate change and the need for sustainable solutions.
Navigating the Little Ice Age: Franklin’s Contextual Challenges
The Little Ice Age posed formidable challenges for early American settlers, compelling them to adapt their lifestyles and technologies. During the severe winters of 1740 and 1741, which saw harbors freeze and food supplies dwindle, Franklin’s invention of the stove emerged as a beacon of ingenuity. As populations expanded and deforestation increased, access to firewood became a pressing concern. Franklin’s prototype offered a solution that promised to enhance heating efficiency while conserving resources, reflecting a deep understanding of environmental history and urgent technological adaptation.
In facing the harsh realities of the Little Ice Age, Franklin preemptively addressed future challenges linked to climate change and resource scarcity. His emphasis on a heating system that consumed less wood while providing greater warmth speaks to a broader ethos of utilizing science to improve living conditions. This not only underscores Franklin’s role as a pioneer in practical science but also reveals how his innovations are foundational for discussions on sustainability in climates facing severe alterations today.
The Legacy of Franklin’s Contributions to Atmospheric Science and Technology: Franklin’s Legacy Lives On
Benjamin Franklin’s significance extends far beyond his more famous inventions, such as the lightning rod; it encompasses his substantial contributions to atmospheric science and technology. His innovative understanding of how air temperature and pressure interact laid groundwork for future meteorological studies. In particular, his insights into the behaviors of heat and air circulation were early steps towards developing the field of environmental science, providing a framework for understanding weather patterns that are increasingly relevant in today’s discussions surrounding climate change.
Chaplin’s exploration of Franklin’s work reveals an astute awareness that the principles governing atmospheric phenomena are central to every invention Franklin put forward, including the pioneering Franklin stove. By recognizing the connection between comfort indoors and climate dynamics outdoors, Franklin’s contributions demonstrate a holistic approach to understanding how human beings can adapt to their environment. This dialogue between science, technology, and the natural world continues to resonate, as audiences today grapple with the implications of human impact on environmental systems and the urgent need for sustainable solutions.
Health and Pollution: Franklin’s Concerns with Emissions
Franklin’s foresight regarding the implications of air quality and health is particularly notable in the context of his stove design. Understanding the relationship between smoke emission and indoor pollution, Franklin endeavored to create a system that minimized hazardous byproducts while maximizing heating efficiency. His approach to re-burning smoke showed a remarkable awareness of environmental and health impacts, making him a precursor to today’s discussions about clean energy and pollution control.
His concerns predate modern environmental awareness, positioning Franklin as a pivotal figure in the history of science’s evolution toward addressing ecological and health considerations. This aspect of his legacy is critical for contemporary discussions about emissions and climate adaptation, as we strive to find innovative solutions to modern pollution challenges. Franklin’s insistence on cleaner burning technologies reminds us that historical figures can provide invaluable insights into our current environmental dilemmas.
Franklin and the Role of Innovation in Societal Progress
The narrative of Benjamin Franklin is not solely about one man’s inventions; it’s about the spirit of innovation that propelled societal progress during his time. In her examination, Joyce Chaplin emphasizes the collective mindset of 18th-century inventors, who believed that ingenuity could combat the pressing challenges posed by their environment. Franklin’s contributions to the heating technology through the Franklin stove exemplify this ethos, representing a blend of practicality and visionary thinking crucial for broader advancements in society.
In light of contemporary issues, which parallel those of Franklin’s era, the importance of innovation remains paramount. Learning from Franklin’s multi-faceted approach can inspire modern scientists and inventors to consider not just immediate solutions, but the long-term implications of their work on society and the environment. Franklin’s legacy urges us to pursue an integrated view of technology that harmonizes human needs with ecological sustainability.
Environmental Adaptation: Reflections from Franklin’s Era
The environmental issues faced by Franklin during the Little Ice Age resonate deeply with today’s climate challenges. Chaplin articulates how Franklin’s response to cold was not merely reactive but indicative of a forward-thinking mindset, anticipating the needs of a warming world. His invention of the Franklin stove embodies a spirit of adaptation, demonstrating how technology can respond to environmental stressors and improve the quality of life for individuals.
This historical perspective serves as a crucial reminder that adaptability, driven by scientific inquiry and innovation, is essential for combating environmental crises. By examining how Franklin navigated the complexities of his environment, we can glean lessons applicable to our own era of climate adaptation. Understanding the interconnectedness of technology, society, and environment remains vital as we seek sustainable pathways to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Lessons from Franklin: Technology and the Modern Climate Crisis
Joyce Chaplin’s research intertwines the narrative of Benjamin Franklin with modern discussions on climate change and technology’s role in addressing it. By comparing Franklin’s innovative spirit with current techno-optimism, she emphasizes warning signs against oversimplified beliefs in single solutions to today’s intricate climate problems. Franklin’s experience—highlighted by his attempt to balance efficiency with environmental health—encourages a multifaceted approach when addressing today’s challenges.
The complexity of climate issues today mirrors the intricacies of Franklin’s world, where multiple solutions are necessary for effective mitigation. Just as Franklin sought various ways to improve indoor heating while minimizing emissions, today’s innovators must embrace a collective approach, harnessing diverse technologies and strategies. Franklin’s legacy challenges us to think beyond the quick fixes and remain vigilant in pursuing comprehensive solutions to ensure a sustainable future.
Culminating Thoughts on Franklin’s Impact on Science and Society
The exploration of Benjamin Franklin’s inventions and contributions, particularly highlighted in Joyce Chaplin’s analysis, reveals the profound impact one individual’s innovative spirit can have on science and society. The Franklin stove, as a practical yet transformative invention, serves as a testament to how technology can not only address immediate needs but also inspire broader understanding of environmental and scientific principles. Franklin’s legacy epitomizes the blend of practicality and enlightenment ideals that fueled progress in the 18th century.
Furthermore, as we examine today’s climate crisis, Franklin’s principles—rooted in a commitment to improve human comfort while considering environmental ramifications—are more relevant than ever. Chaplin’s insights encourage a reevaluation of our approach to science and innovation, urging us to foster an enduring legacy of progress that prioritizes sustainable solutions. Franklin’s life and work exemplify how the fusion of science, technology, and humanity can navigate the complexities of environmental challenges across centuries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key features of the Franklin stove developed by Benjamin Franklin?
The Franklin stove, invented by Benjamin Franklin, is known for its unique design that features a flatpack of iron plates. This innovative invention allowed colonists to easily assemble the stove and insert it into their existing hearths for improved heating efficiency. The stove was designed to burn less wood than traditional fireplaces while providing greater warmth, showcasing Franklin’s commitment to creating more effective heating solutions during the harsh winters.
How did the Franklin stove contribute to environmental history?
The Franklin stove holds significance in environmental history as it was designed during the cold winter of 1740-41, a period marked by extreme temperatures and deforestation. Franklin’s invention aimed to reduce the consumption of firewood, addressing the environmental consequences of wood shortages for settlers, particularly the poor. By creating a more efficient heating solution, the Franklin stove represents an early adaptation to climate challenges.
What scientific principles did Benjamin Franklin apply in the design of his stove?
In designing the Franklin stove, Benjamin Franklin applied the principle of convection, which involves warm air rising and creating a circulation pattern. He aimed to optimize indoor temperatures by ensuring that heat would distribute evenly throughout a room. This scientific understanding not only contributed to better heating practices but also deepened Franklin’s explorations into weather patterns and atmospheric phenomena.
In what ways does Joyce Chaplin’s book highlight the significance of the Franklin stove?
Joyce Chaplin’s book, ‘The Franklin Stove: An Unintended American Revolution,’ emphasizes the stove’s role in changing perceptions about technology and comfort during the 18th century. Chaplin argues that Franklin’s seemingly modest invention was pivotal in fostering new ideas about heating, environmental adaptation, and technological innovation, illustrating Franklin’s broader contributions to the history of science.
How did Franklin’s stove design respond to climate adaptation needs in the 18th century?
Franklin’s stove was a direct response to the climate adaptation needs of the 18th century, particularly during the extreme winter of 1740-41. By creating a stove that required less firewood but provided more heat, Franklin’s invention addressed the issue of heating efficiency while also anticipating the future challenges of resource shortages due to deforestation and increased settlement.
What impact did the Franklin stove have on subsequent inventions and technology?
The design of the Franklin stove influenced future heating technologies by introducing concepts of efficiency and environmental consideration. By later versions of the stove, Franklin sought to minimize emissions by re-burning smoke, paving the way for discussions on pollution and energy efficiency that are still relevant in today’s climate discourse. His innovation inspires ongoing exploration into sustainable technology.
How does the Franklin stove reflect Benjamin Franklin’s views on science and innovation?
The Franklin stove exemplifies Benjamin Franklin’s belief that science and innovation could greatly enhance human comfort and societal well-being. His experimental approach to design, grounded in scientific principles, shows that he saw technology as not merely functional but as a means to improve the quality of life, further inspiring the scientific achievements that arose during the Enlightenment.
What lessons can modern inventors learn from the history of the Franklin stove?
Modern inventors can learn from the history of the Franklin stove the importance of considering long-term impacts and multiple solutions to environmental challenges. Franklin’s approach encourages vigilance in monitoring technology’s effectiveness, suggesting that sustainable innovation requires diverse strategies rather than reliance on a single solution to address climate change.
How does the Franklin stove relate to Benjamin Franklin’s other inventions?
The Franklin stove is often overshadowed by Franklin’s more famous inventions, such as the lightning rod and bifocals, but it holds equal importance in illustrating his ingenuity. Like his other inventions, the stove reflects Franklin’s ability to blend practical needs with scientific inquiry, making it a crucial part of his legacy as a pioneer in technology and environmental awareness.
What role did the Franklin stove play in the context of 18th-century American society?
In 18th-century American society, the Franklin stove played a crucial role in improving indoor heating for colonists during brutal winters. By making heating more efficient and accessible, it not only enhanced comfort but also signified a shift in how people viewed their relationship with technology and the environment, promoting a mindset of adaptation and innovation in the face of climate challenges.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Joyce Chaplin’s book discusses Benjamin Franklin’s invention of the stove and its historical context. |
| The Franklin stove was a response to severe cold winters, designed to improve heating efficiency for colonists. |
| Franklin’s stove contributed to understanding atmospheric science, influencing ideas about indoor and outdoor heat distribution. |
| The book highlights Franklin’s multifaceted legacy, combining scientific inquiry with social awareness and technology. |
| Chaplin argues the stove was a critical invention that symbolized human ingenuity and adaptation to climate change. |
| Franklin’s efforts to minimize smoke emissions in his later stove designs reflect early environmental awareness. |
| The narrative indicates that one must consider multiple solutions to address today’s climate issues, echoing Franklin’s innovative spirit. |
Summary
The Franklin stove is not just a familiar name in American history; it represents a pivotal evolution in heating technology that adapted to climate challenges of its time. Joyce Chaplin’s exploration highlights how Franklin’s ingenious design relates to atmospheric science, leading to a broader understanding of both indoor comfort and environmental dynamics. By minimizing smoke emissions, Franklin advanced early efforts in environmental awareness, illustrating a forward-thinking approach that resonates with today’s climate discourse. Ultimately, the Franklin stove serves as a symbol of the inventive spirit necessary to tackle modern environmental challenges.